-
-23%


Gabinete de estación de bloqueo y etiquetado con 70 dispositivos LOTO
Precio habitual $369.95Precio habitual$479.95-23%Precio de oferta $369.95 -
Agotado

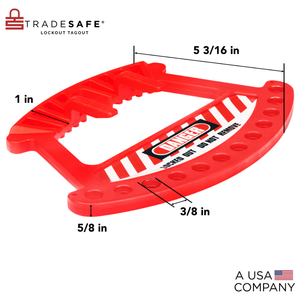
Almacenamiento portátil de candados de seguridad: se adapta a 12 candados de bloqueo
Precio habitual $22.95Precio habitual$39.00-41%Precio de oferta $22.95 -
-75%


Bolsa con cincha para bloqueo y etiquetado, 17-1/4” x 10”
Precio habitual $24.95Precio habitual$100.00-75%Precio de oferta $24.95 -
-70%


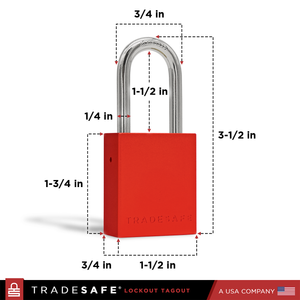
Bloqueo de botón pulsador – Redondo – Mediano
Precio habitual $35.80Precio habitual$120.00-70%Precio de oferta $35.80 -
-65%
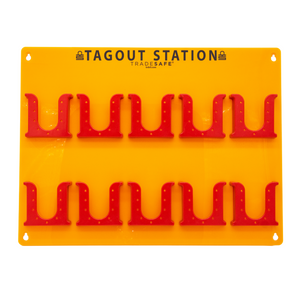
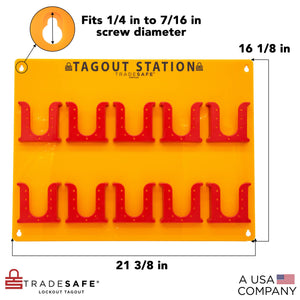
Estación de bloqueo y etiquetado para etiquetas LOTO - Etiquetas no incluidas
Precio habitual $69.95Precio habitual$199.00-65%Precio de oferta $69.95 -
Agotado

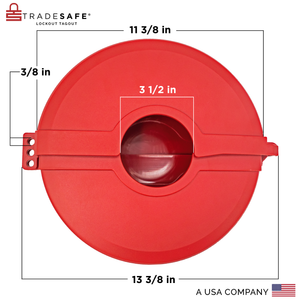
Bloqueo de válvula de compuerta: diámetro de manija de válvula de 6-½” a 10”
Precio habitual $54.95Precio habitual$109.00-50%Precio de oferta $54.95 -
Agotado

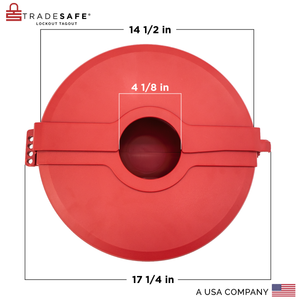
Bloqueo de válvula de compuerta: diámetro de manija de válvula de 10" a 13"
Precio habitual $64.95Precio habitual$119.00-45%Precio de oferta $64.95 -
-27%


Kit profesional de bloqueo y etiquetado: 2 llaves por candado
Precio habitual $239.95Precio habitual$329.95-27%Precio de oferta $239.95 -
-62%


Keyed Alike Lockout Locks - 10 White Padlocks - 2 Keys Per Lock
Precio habitual $59.95Precio habitual$159.00-62%Precio de oferta $59.95 -
-23%


Estación de bloqueo y etiquetado de candados de seguridad - Se adapta a 20 candados - Candados LOTO incluidos
Precio habitual $153.95Precio habitual$199.00-23%Precio de oferta $153.95 -
-49%


Bloqueo de botón pulsador - Redondo - Juego de 3 piezas
Precio habitual $29.95Precio habitual$59.00-49%Precio de oferta $29.95 -
-42%


Estación de bloqueo y etiquetado: grande
Precio habitual $77.95Precio habitual$135.00-42%Precio de oferta $77.95 -
-62%

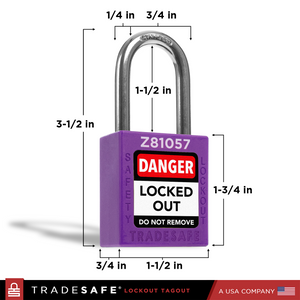
Juego de candados de bloqueo y etiquetado con llaves iguales - 10 candados morados - 2 llaves por candado
Precio habitual $59.95Precio habitual$159.00-62%Precio de oferta $59.95 -
-49%

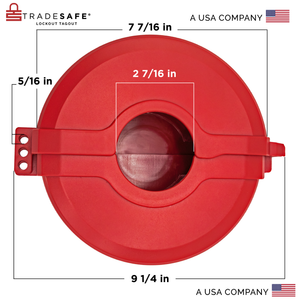
Bloqueo de válvula de compuerta: diámetro de manija de válvula de 5" a 6-½"
Precio habitual $29.95Precio habitual$59.00-49%Precio de oferta $29.95 -
-40%
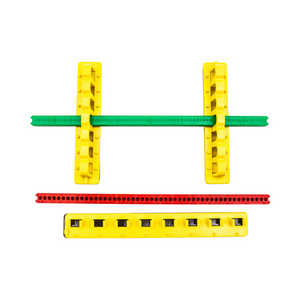
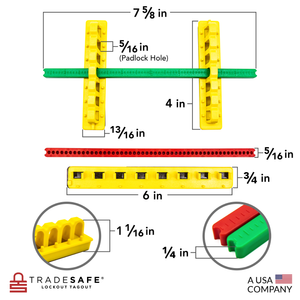
Bloqueo de disyuntores - Kit de bloqueo de disyuntores - 480/600 voltios
Precio habitual $29.95Precio habitual$50.00-40%Precio de oferta $29.95 -
-51%

Juego de candados de bloqueo y etiquetado con diferentes llaves - 10 candados de seguridad rojos - 2 llaves por candado
Precio habitual $77.95Precio habitual$159.00-51%Precio de oferta $77.95 -
-26%


Kit profesional de bloqueo y etiquetado: 2 llaves por candado
Precio habitual $319.95Precio habitual$429.95-26%Precio de oferta $319.95 -
-62%

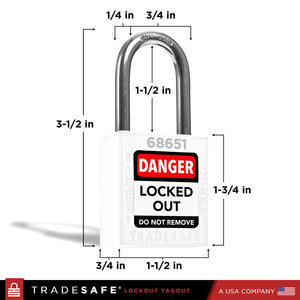
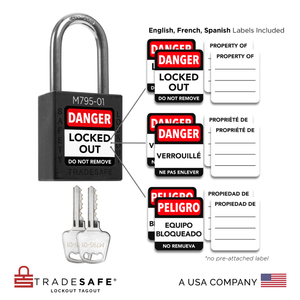
Keyed Different Lockout Locks - 10 White Padlocks - 2 Keys Per Lock
Precio habitual $59.95Precio habitual$159.00-62%Precio de oferta $59.95 -
-54%

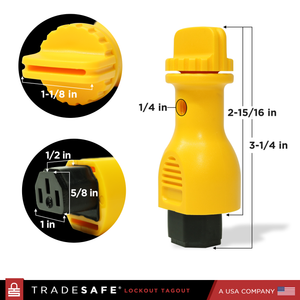
Power Cord Plug Lockout Device - 1 Pack
Precio habitual $22.95Precio habitual$50.00-54%Precio de oferta $22.95 -
-51%

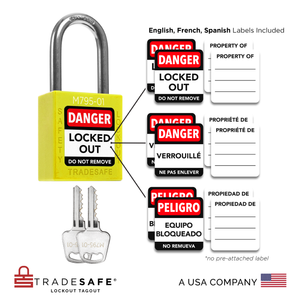
Juego de candados de bloqueo y etiquetado con diferentes llaves - 10 candados de seguridad rojos - 2 llaves por candado
Precio habitual $77.95Precio habitual$159.00-51%Precio de oferta $77.95 -
-51%

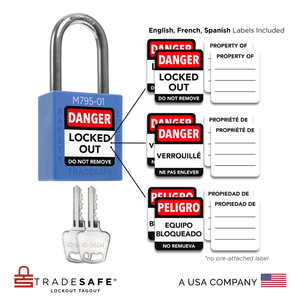
Juego de candados de bloqueo y etiquetado con diferentes llaves - 10 candados de seguridad rojos - 2 llaves por candado
Precio habitual $77.95Precio habitual$159.00-51%Precio de oferta $77.95 -
-52%


Juego de candados de bloqueo y etiquetado con llaves iguales - 10 candados amarillos - 2 llaves por candado
Precio habitual $94.95Precio habitual$199.00-52%Precio de oferta $94.95 -
-14%


Gabinete de la estación de bloqueo y etiquetado: no se incluyen dispositivos de bloqueo y etiquetado
Precio habitual $299.95Precio habitual$349.95-14%Precio de oferta $299.95 -
-33%


Gabinete de estación de bloqueo y etiquetado con 70 dispositivos LOTO
Precio habitual $159.95Precio habitual$239.95-33%Precio de oferta $159.95 -
-23%

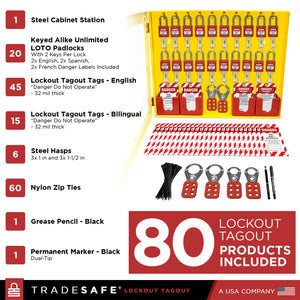
Gabinete de estación de bloqueo y etiquetado con 70 dispositivos LOTO
Precio habitual $369.95Precio habitual$479.95-23%Precio de oferta $369.95 -
-14%


Bolsa de bloqueo y etiquetado - Bolsa de bloqueo roja
Precio habitual $59.95Precio habitual$70.00-14%Precio de oferta $59.95 -
-47%


Confined Space Cover
Precio habitual $39.95Precio habitual$75.00-47%Precio de oferta $39.95 -
-64%


Keyed Alike Unlimited Lockout Locks - 10 White Padlocks - 2 Keys Per Lock
Precio habitual $59.95Precio habitual$165.00-64%Precio de oferta $59.95 -
-62%


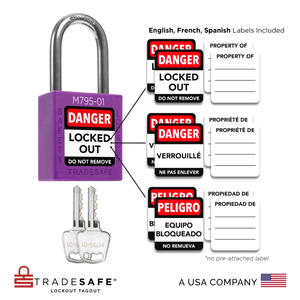
Lockout Tagout Padlock Labels - English, Spanish, French - Pack of 60
Precio habitual $18.95Precio habitual$50.00-62%Precio de oferta $18.95 -
Agotado

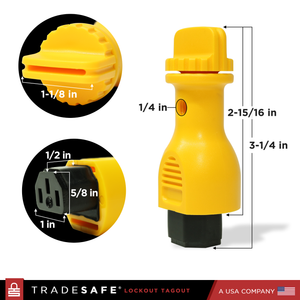
Power Cord Plug Lockout Device - 5 Pack
Precio habitual $79.95Precio habitual$150.00-47%Precio de oferta $79.95 -
-49%


Nylon Drum Security Plug With 2 Rubber Gaskets
Precio habitual $15.95Precio habitual$31.50-49%Precio de oferta $15.95 -
-51%

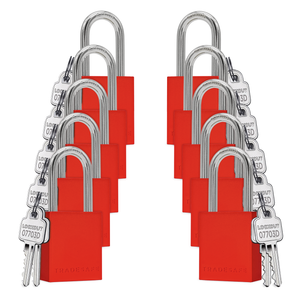
Juego de candados de bloqueo y etiquetado con diferentes llaves - 10 candados de seguridad rojos - 2 llaves por candado
Precio habitual $77.95Precio habitual$159.00-51%Precio de oferta $77.95 -
-52%


Juego de candados de bloqueo y etiquetado con llaves iguales - 10 candados amarillos - 2 llaves por candado
Precio habitual $94.95Precio habitual$199.00-52%Precio de oferta $94.95 -
-52%


Juego de candados de bloqueo y etiquetado con llaves iguales - 10 candados amarillos - 2 llaves por candado
Precio habitual $94.95Precio habitual$199.00-52%Precio de oferta $94.95 -
-52%


Juego de candados de bloqueo y etiquetado con llaves iguales - 10 candados amarillos - 2 llaves por candado
Precio habitual $94.95Precio habitual$199.00-52%Precio de oferta $94.95 -
-52%
Juego de candados de bloqueo y etiquetado con llaves iguales - 10 candados amarillos - 2 llaves por candado
Precio habitual $94.95Precio habitual$199.00-52%Precio de oferta $94.95 -
-25%


Estación de bloqueo y etiquetado - XL
Precio habitual $399.95Precio habitual$529.95-25%Precio de oferta $399.95 -
-17%


Bolsa de bloqueo y etiquetado - Bolsa de bloqueo roja
Precio habitual $49.95Precio habitual$60.00-17%Precio de oferta $49.95 -
-51%


Keyed Different Lockout Locks with Master Keys - 10 White Padlocks - 2 Keys Per Lock
Precio habitual $77.95Precio habitual$159.00-51%Precio de oferta $77.95 -
-43%


Power Plug Lock Keyed Alike Unlimited - 5 Pack - 2 Keys Each
Precio habitual $84.95Precio habitual$150.00-43%Precio de oferta $84.95 -
-49%

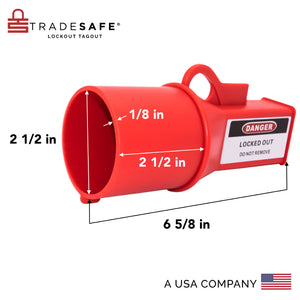
Dispositivo de bloqueo de salida eléctrica: diámetro del cuerpo de 2½”
Precio habitual $24.95Precio habitual$49.00-49%Precio de oferta $24.95 -
-36%


Estación de bloqueo y etiquetado para etiquetas LOTO: 150 etiquetas incluidas
Precio habitual $189.95Precio habitual$299.00-36%Precio de oferta $189.95 -
-51%

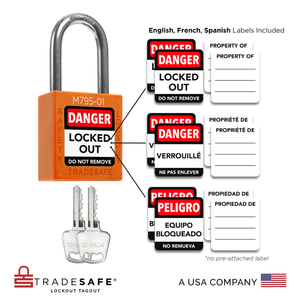
Juego de candados de bloqueo y etiquetado con diferentes llaves - 10 candados de seguridad rojos - 2 llaves por candado
Precio habitual $77.95Precio habitual$159.00-51%Precio de oferta $77.95 -
Agotado

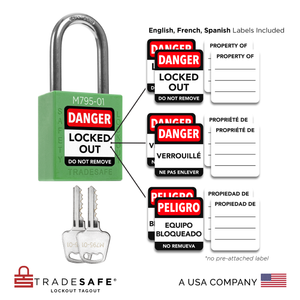
Juego de candados de bloqueo y etiquetado con diferentes llaves - 10 candados de seguridad rojos - 2 llaves por candado
Precio habitual $77.95Precio habitual$159.00-51%Precio de oferta $77.95 -
-50%

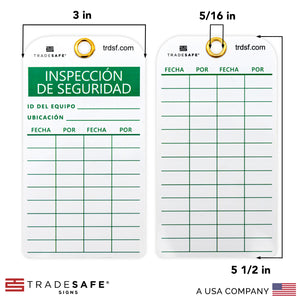
Etiquetas de Inspección de Seguridad Españolas – Paquete de 30
Precio habitual $29.95Precio habitual$60.00-50%Precio de oferta $29.95 -
-50%

Etiquetas bilingües de inspección de seguridad - Paquete de 30
Precio habitual $29.95Precio habitual$60.00-50%Precio de oferta $29.95 -
-42%


OSHA GHS Hazcom Poster
Precio habitual $28.95Precio habitual$50.00-42%Precio de oferta $28.95 -
-42%


Pictogramas GHS Póster
Precio habitual $28.95Precio habitual$50.00-42%Precio de oferta $28.95
El programa de bloqueo y etiquetado es un componente importante de sus prácticas de seguridad para mantener su lugar de trabajo seguro y compatible con OSHA. Sirve para proteger a los trabajadores de la energía peligrosa no controlada que puede escapar de la maquinaria o el equipo durante el aislamiento, el servicio o el mantenimiento. Como resultado, es fundamental que los trabajadores tengan acceso a los suministros correctos de bloqueo y etiquetado, así como la capacitación LOTO adecuada, en sus áreas de trabajo.
En TRADESAFE , la seguridad nunca se compromete sino que se maximiza. Nuestra colección incluye una amplia gama de información de seguridad de bloqueo y etiquetado y soluciones disponibles para adaptarse a enchufes y enchufes, válvulas, paneles, disyuntores y más. Cada dispositivo de bloqueo y etiquetado es fácil de usar y está fabricado con materiales de alta calidad que pueden resistir los entornos hostiles y peligrosos comunes en las instalaciones industriales.
TRADESAFE solo ofrece suministros LOTO de primera calidad diseñados con precisión para ayudarlo a cumplir con los estándares OSHA 1910.147 (Control de energía peligrosa) en su lugar de trabajo y al mismo tiempo inculcar responsabilidad y rendición de cuentas entre sus trabajadores. Obtenga un socio de seguridad confiable con TRADESAFE .
































































































